Hi Folks!
This blog post is regarding the basics of SOLR setup and using the SOLR.Net.
So, let us get started!
Download the SOLR 5.5 from below URL. (You can give it a try with latest version else first use one)
https://archive.apache.org/dist/lucene/solr/5.5.0/
- Extract the downloaded file to some location. In my case it is D:\learning\Search in dot net\solr-5.5.0.
- Setup JAVA_HOME environment variable. To do so, follow this link.
- Open CMD as admin from the SOLR bin folder
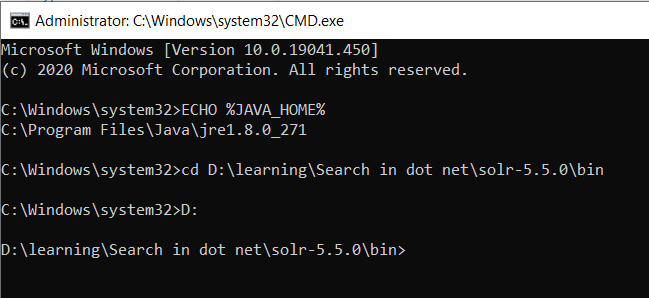
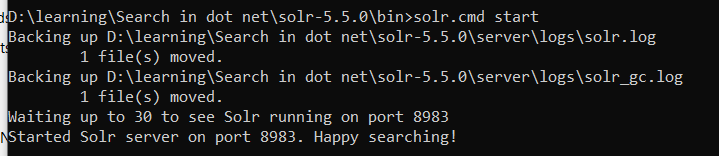
- You should find solr.cmd from SOLR bin folder. Run below command from cmd
>solr.cmd start
- Open the below URL in any browser

- Run below command to create the core
>solr.cmd create -c articles
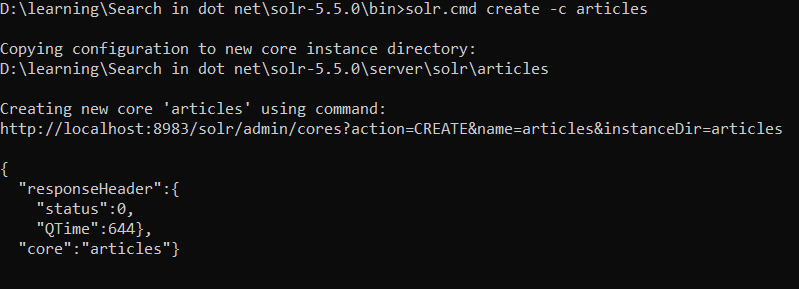

Go to http://localhost:8983/solr/#/
And refresh the page.
You should see the core created as above.
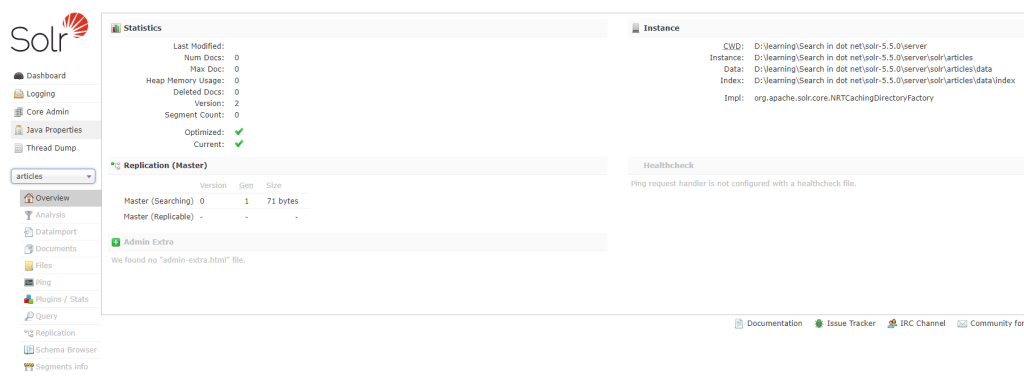
- Create .NET framework console app.
- Right click project node, go to nuget manager. Search for Solr.Net and install the latest stable package.
- Copy below Article Class to your source file.
public class Article
{
[SolrUniqueKey("articleid")]
public string CourseId { get; set; }
[SolrField("articleTitle")]
public string CourseTitle { get; set; }
[SolrField("articleDescription")]
public int DurationInSeconds { get; set; }
[SolrField("publishDate")]
public DateTime ReleaseDate { get; set; }
}
- Import required namespaces.
- Go to below as highlighted to confirm we don’t have any data.
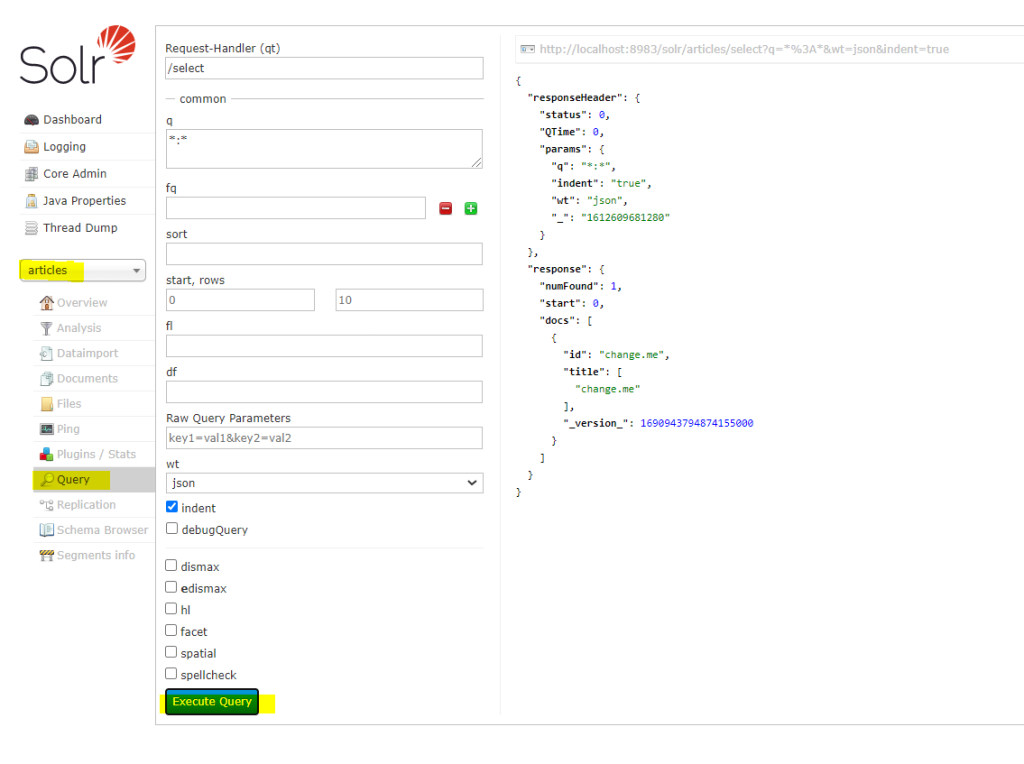
- Write below code in your project
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Indexing the content");
IndexArticles();
Console.WriteLine("Searching the content");
}
private static void IndexArticles()
{
List<Article> allArticles = new List<Article>();
FillAllArticles(allArticles);
Startup.Init<Article>("http://localhost:8983/solr/articles");
ISolrOperations<Article> solr = ServiceLocator.Current.GetInstance<ISolrOperations<Article>>();
foreach (Article article in allArticles)
{
solr.Add(article);
}
solr.Commit();
}
private static void FillAllArticles(List<Article> allArticles)
{
allArticles.Add(new Article { Articleid=Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), ArticleDescription="article 1 descripton", ArticleTitle="article 1 title", PublishDate=DateTime.Now});
allArticles.Add(new Article { Articleid = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), ArticleDescription = "article 2 descripton", ArticleTitle = "article 2 title", PublishDate = DateTime.Now });
}
}
- Build and execute the project.
- Now go back to Solr Dashboard and refresh the core. You should see the inserted data.
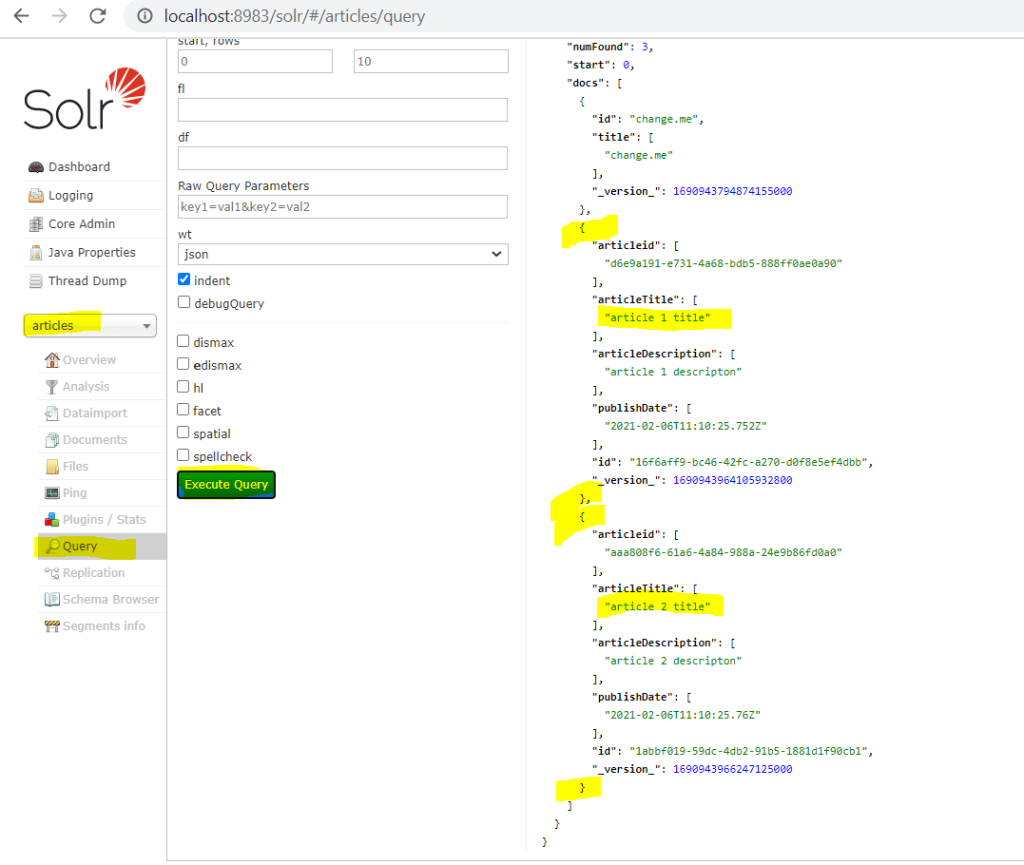
- Now comment out the first two lines in main method
//Console.WriteLine("Indexing the content");
//IndexArticles();
- We will now read the data
Copy below code in your main method. Build and run it in debug mode for now.
Startup.Init<Article>("http://localhost:8983/solr/articles");
ISolrOperations<Article> solr = ServiceLocator.Current.GetInstance<ISolrOperations<Article>>();
Console.WriteLine("Please enter search phrase:");
string userInput = Console.ReadLine();
while (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(userInput))
{
SolrQueryResults<Article> Articles = solr.Query(userInput);
int i = 0;
foreach (Article Article in Articles)
{
Console.WriteLine(i++ + ": " + Article.ArticleTitle + " "+ Article.ArticleDescription);
}
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine + "Please enter search phrase:");
userInput = Console.ReadLine();
}
- Enter search phrase and enter, you will get below error

The reason is the configuration of article fields has multiValued = true by default.
- Let us disable it from the configuration itself.
Go to article managed-schema file. In my case it is D:\learning\Search in dot net\solr-5.5.0\server\solr\articles\conf\managed-schema
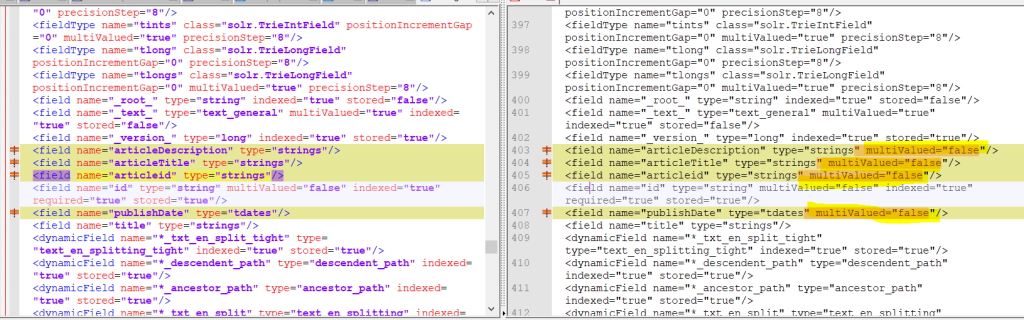
Provide multiValued=”false” to the above fields.
Save it.
- To pick up new configuration we should restart the SOLR server. Close the cmd running the solr.
- Open cmd as admin from SOLR bin folder. Run below command from cmd
>solr.cmd start
- Now rerun the console application. We should be able to search.

Happy Basic Indexing and Searching!